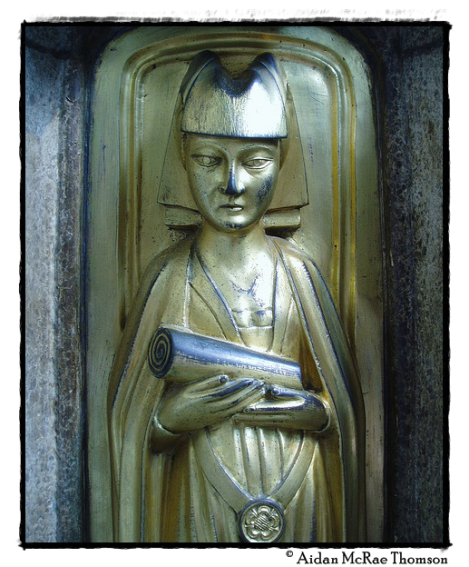

Detail of the magnificent tomb chest that bears the effigy of Richard Beauchamp, 13th Earl of Warwick in the chapel he founded at St Mary’s, Warwick. This effigy is that of his daughter-in-law, Lady Cecily Neville.
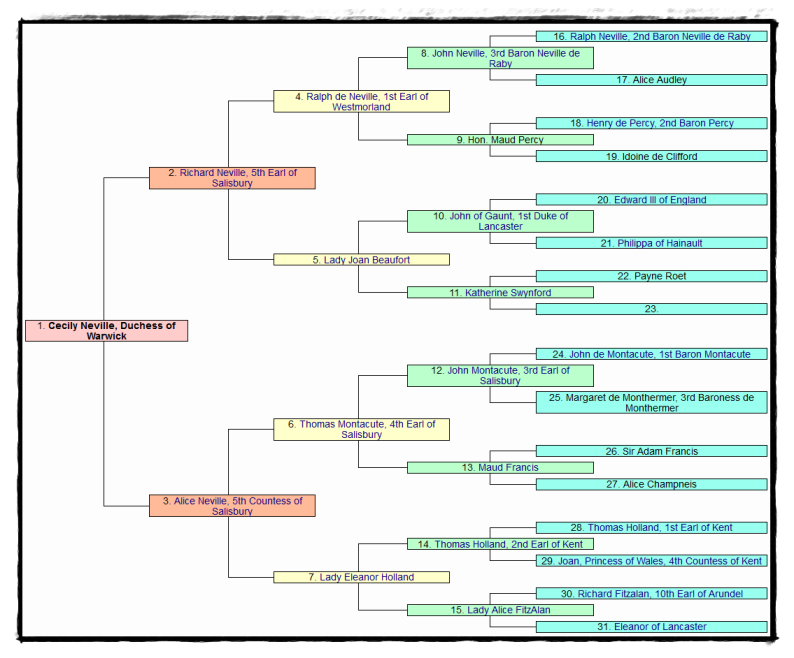
Lady Cecily Neville, Duchess of Warwick, Countess of Worcester (c.1425[2][5] – 26 July 1450[3]) was the second child and daughter of Sir Richard Neville, 5th Earl of Salisbury and Lady Alice Montacute, suo jure 5th Countess of Salisbury.[2] Her nine siblings included Richard Neville, 16th Earl of Warwick; John Neville, 1st Marquess of Montagu; George Neville, (Archbishop of York and Chancellor of England); Sir Thomas Neville; Lady Joan, Countess of Arundel; Lady Katherine, Baroness Hastings; Lady Alice, Baroness FitzHugh; Lady Eleanor, Countess of Derby; and Lady Margaret, Countess of Oxford.[2]
She was most likely named after her paternal aunt, Lady Cecily Neville, later Duchess of York.[2] Her first cousins by the Duchess of York included Anne of York; Edmund, Earl of Rutland; Elizabeth of York; Margaret of York; George Plantagenet, 1st Duke of Clarence; and Kings Edward IV and Richard III. Other cousins included John Mowbray, 3rd Duke of Norfolk; Lord Humphrey Stafford, 7th Earl of Stafford [father of 2nd Duke of Buckingham]; Lady Katherine Stafford, Countess of Shrewsbury [wife of the 3rd Earl]; Henry Percy, 3rd Earl of Northumberland; Ralph, 2nd Earl of Westmorland; George Neville, 4th and 2nd Baron of Abergavenny; Thomas Dacre, 1st Baron Dacre of Gillesland; and Ralph Greystoke, 5th Baron.
In 1436, it was decided that Cecily would marry Henry de Beauchamp, Lord Despenser (later 1st Duke of Warwick and King of the Isle of Wight, as well as of Jersey and Guernsey).[2] Henry was the son and heir of son of Richard de Beauchamp, 13th Earl of Warwick and Lady Isabel le Despenser, the sole heiress of Thomas le Despenser, 1st Earl of Gloucester (d.1399) by his wife, Constance of York. At the same time, it was decided that her elder brother, Richard, would marry Beauchamp’s younger sister, Lady Anne.[2] The marriage negotiations were not easy or inexpensive; Salisbury had to promise to pay Warwick a large sum of 4, 700 marks (£3, 233.66).[2] In 1436, the two couples married in a double marriage ceremony.[2]
Warwick Inheritance
The advantage of this marriage, which came in the form of Cecily’s husband being created Duke of Warwick on 14 April 1445, was short lived as her husband died on 11 June 1446 and the couple’s only daughter, Lady Anne Beauchamp, was allowed to succeed only as suo jure 15th Countess of Warwick. Upon the death of Cecily’s daughter in 1449, the title was inherited by her paternal aunt, also named Lady Anne Beauchamp. Lady Anne, who had married Cecily’s brother Sir Richard Neville, becamesuo jure 16th Countess of Warwick thus making Neville jure uxoris 16th Earl of Warwick. There were no objections as the elder half-sisters from the 13th Earl of Warwick’s marriage to his first wife, Elizabeth Berkeley; their husband’s, John Talbot, 1st Earl of Shrewsbury and Edmund Beaufort, 2nd Duke of Somerset, were off defending Normandy.[2] The third half-sister had been married to George Neville, 1st Baron Latimer who had been declared insane and his brother Salisbury already possessed his lands.[2] The three sisters had to settle for nine manors, while the Despenser lands were preserved for George Neville, later 4th Baron Bergavenny, the heir of the 16th Countess of Warwick’s maternal sister, Lady Elizabeth Beauchamp, suo jure Baroness Bergavenny.[2] Cecily and her second husband, the Earl of Worcester, however had custody of the land up until two months before Cecily died in July 1540.[2] Upon that time, the lands were handed over to Cecily’s brother, Warwick.[2] However in 1457, when Bergavenny became of age — the rights were ignored and Warwick’s wife, Anne, became the sole heiress of her mother’s inheritance in the first parliament of Edward IV in 1461.[2] Both Warwick and Bergavenny were cousins to the King, however Warwick was the older brother of Bergavenny’s father. Warwick’s wife was also the daughter of the 13th Earl of Warwick, who was senior to his cousin, Richard Beauchamp, 1st Earl of Worcester — first husband of Lady Isabel le Despenser.
Warwick was a supporter of the House of York until the Battle of Barnet when he and Oxford both sided with the Lancastrian King.[2]
Her second husband was John Tiptoft, 1st Earl of Worcester. They had no children.
Lady Cecily, the Dowager Duchess of Warwick and Countess of Worcester was buried in 1450 with her first husband, the Duke of Warwick, at Tawkesbury Abbey; no monument.[1] Warwick was buried at his own request between the stalls in the choir in 1446. At the time the choir was repaved in 1875, a grave of stone filled with rubble was found together with some bones of a man of herculean size. These, no doubt, were those of the Duke who was buried here. The large marble slab that formerly covered the grave disappeared early in this century but the brasses that were originally in it had been taken away long before, Cecily, the Dowager Duchess of Warwick was buried in the same place on 31 July 1450.[3][4]
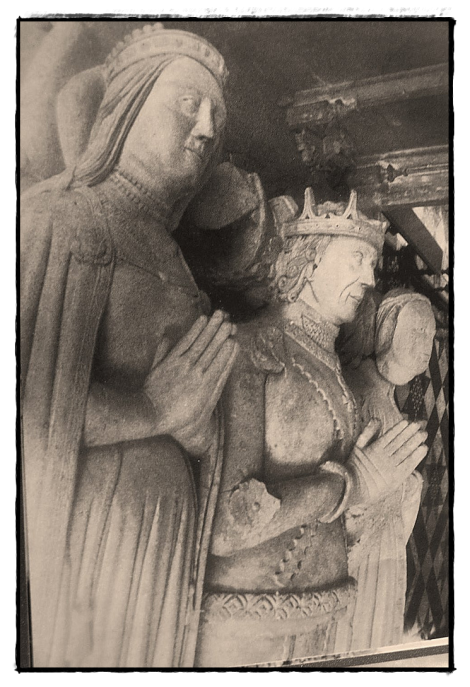

Effigy of John Tiptoft and his second and third wives, Elizabeth Greyndour and Elizabeth Hopton at Ely Cathedral
Cecily is portrayed on the tomb of her father-in-law, Richard Beauchamp, 13th Earl of Warwick, within the Chapel. The Purbeck Marble tomb chest is decorated with a superb and complete set of 14 gilt bronze mourners (all male to the south, all female to the north) complimented by 18 smaller figures of angels. The mourners are identified by their enamelled coats of arms which survive beneath them. English medieval bronze sculpture of this kind (c.1460), of this quality and in such excellent preservation is extremely rare! (Aidan McRae Thomson)
The 1448 contract for making this tomb survives: it indicates that it is not a portrait and refers to the following who were involved in its making: John Bourde of Corfe supplied the Purbeck Marble, William Austen of London cast the metal, John Massingham, carver, made the model, Bartholomew Lambespring, goldsmith, polished and gilded the effigy; one Roger Webb is also referred to in this contract but it is not known what his role was in the construction. A separate contract of the following year with William Austen to cast the effigy. A third contract of 1453 is for brass plates for the lid, sides and the hearse; in this contract John Essex of London, marbler and Thomas Stevyns of London, coppersmith, also appear with William Austen.
Cast gilt bronze effigy in armour on a Purbeck marble tomb chest. The Earl’s hands are held in a curious separated position. Head on helmet with crest of a swan and his feet on both a bear and griffin. The details of the armour are very fine. Charles Stothard lifted the effigy down from the tomb chest to draw its dorsal surface where the armour is again shown in very fine detail. Over the whole is a hooped framework – the ‘hearse’ referred to above; this would have supported a fabric cover and only be removed when masses were said for his soul. Around the tomb chest are gilt bronze ‘mourners’ – seven male and seven female. The mourners include the 13th Earl’s children and in-laws. They include [among others] his son Henry who became Duke of Warwick, his daughter-in-law Duchess Cecily [daughter of the 5th Earl of Salisbury], the 5th Earl and Countess of Salisbury [Richard Neville and Lady Alice Montacute], his daughter Lady Anne [sister of the Duke] and her husband Richard Neville [brother of Duchess Cecily], who inherited the Beauchamp estates to become Earl and Countess of Warwick.[6]
Richard Beauchamp fought with Henry IV and Henry V and was guardian of the infant Henry VI. At the time of his death he was Governor of Normandy.
Cast gilt bronze effigy in armour on a Purbeck marble tomb chest. The Earl’s hands are held in a curious separated position. Head on helmet with crest of a swan and his feet on both a bear and griffin. The details of the armour are very fine. Charles Stothard lifted the effigy down from the tomb chest to draw its dorsal surface where the armour is again shown in very fine detail. Over the whole is a hooped framework – the ‘hearse’ referred to above; this would have supported a fabric cover and only be removed when masses were said for his soul. Around the tomb chest are gilt bronze ‘mourners’ – seven male and seven female. The mourners include the 13th Earl’s children and in-laws. They include [among others] his son Henry who became Duke of Warwick, his daughter-in-law Duchess Cecily [daughter of the 5th Earl of Salisbury], the 5th Earl and Countess of Salisbury [Richard Neville and Lady Alice Montacute], his daughter Lady Anne [sister of the Duke] and her husband Richard Neville [brother of Duchess Cecily], who inherited the Beauchamp estates to become Earl and Countess of Warwick.[6]
Richard Beauchamp fought with Henry IV and Henry V and was guardian of the infant Henry VI. At the time of his death he was Governor of Normandy.
References
- Henri Jean Louis Joseph Massé. “The Abbey Church of Tewkesbury:with some account of the Priory Church of Deerhurst, Gloucestershire,” G. Bell. 1906. pg 79.
- David Baldwin. “The Kingmaker’s Sisters: Six Powerful Women in the Wars of the Roses,” The History Press; First Edition edition, 1 August 2009.
- Michael Hicks. “Warwick, the Kingmaker,” John Wiley & Sons, 15 April 2008. pg 47.
- G.E. Cokayne; with Vicary Gibbs, H.A. Doubleday, Geoffrey H. White, Duncan Warrand and Lord Howard de Walden, editors, The Complete Peerage of England, Scotland, Ireland, Great Britain and the United Kingdom, Extant, Extinct or Dormant, new ed., 13 volumes in 14 (1910-1959; reprint in 6 volumes, Gloucester, U.K.: Alan Sutton Publishing, 2000), volume XII/2, page 845.
- The eldest child of the Salisbury’s, Lady Joan (later Countess of Arundel) was born before 2 November 1424. Lady Cecily, the second child, was followed by Richard Neville (later 16th Earl of Warwick) in 1428. Cecily is noted to be born shortly after Joan in Baldwin’s “The Kingmaker’s Sisters.“
- Anne MacGee Morganstern, John A. A. Goodall. “Gothic Tombs of Kinship in France, the Low Countries, and England,” Penn State Press, Jan 1, 2000. pg 137.
- Aidan McRae Thomson. Beauchamp Tomb: Duchess Cecily of Warwick, 20 June 2008.
- “A description of the Collegiate Church and choir of St. Mary, Warwick & Beauchamp Chapel,” 1841. pg 20.
No comments:
Post a Comment